Setup VPC Peering
Connecting two different networks
In this tutorial, we will use an EC2 instance in the development environment to control an EC2 instance in the production environment for deploying the application server. Therefore, we need to create a peering connection so that devices in both VPCs can communicate with each other.
In the VPC console:
- Select Peering connection
- Click Create peering connection
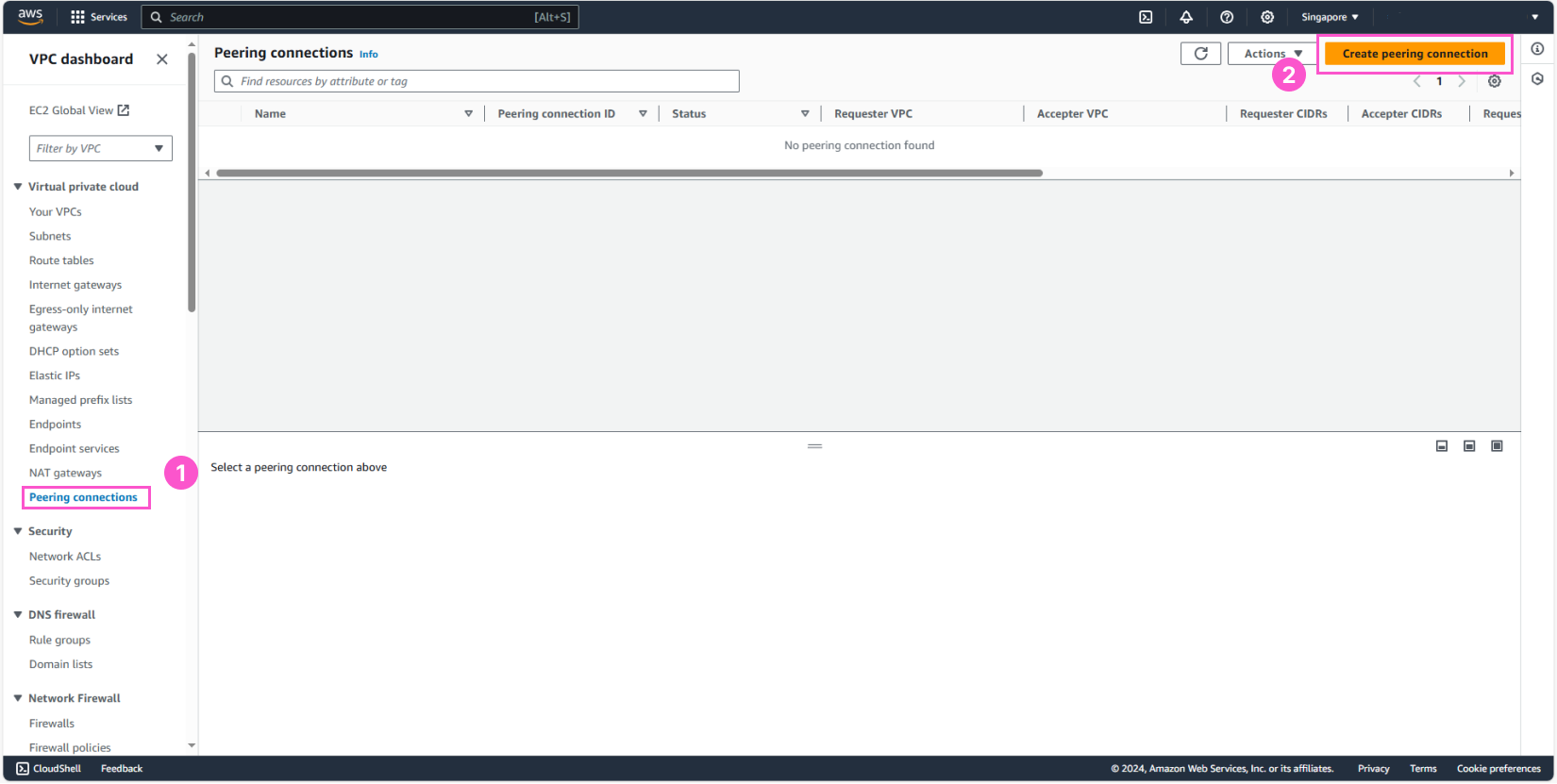
In the settings:
- Name:
dev-prod-peering - In Select a local VPC to peer with, choose production-vpc
- In Select another VPC to peer with, choose:
- Account: My Account
- Region: This Region (ap-southeast-1)
- In VPC ID (Accepter), select development-vpc
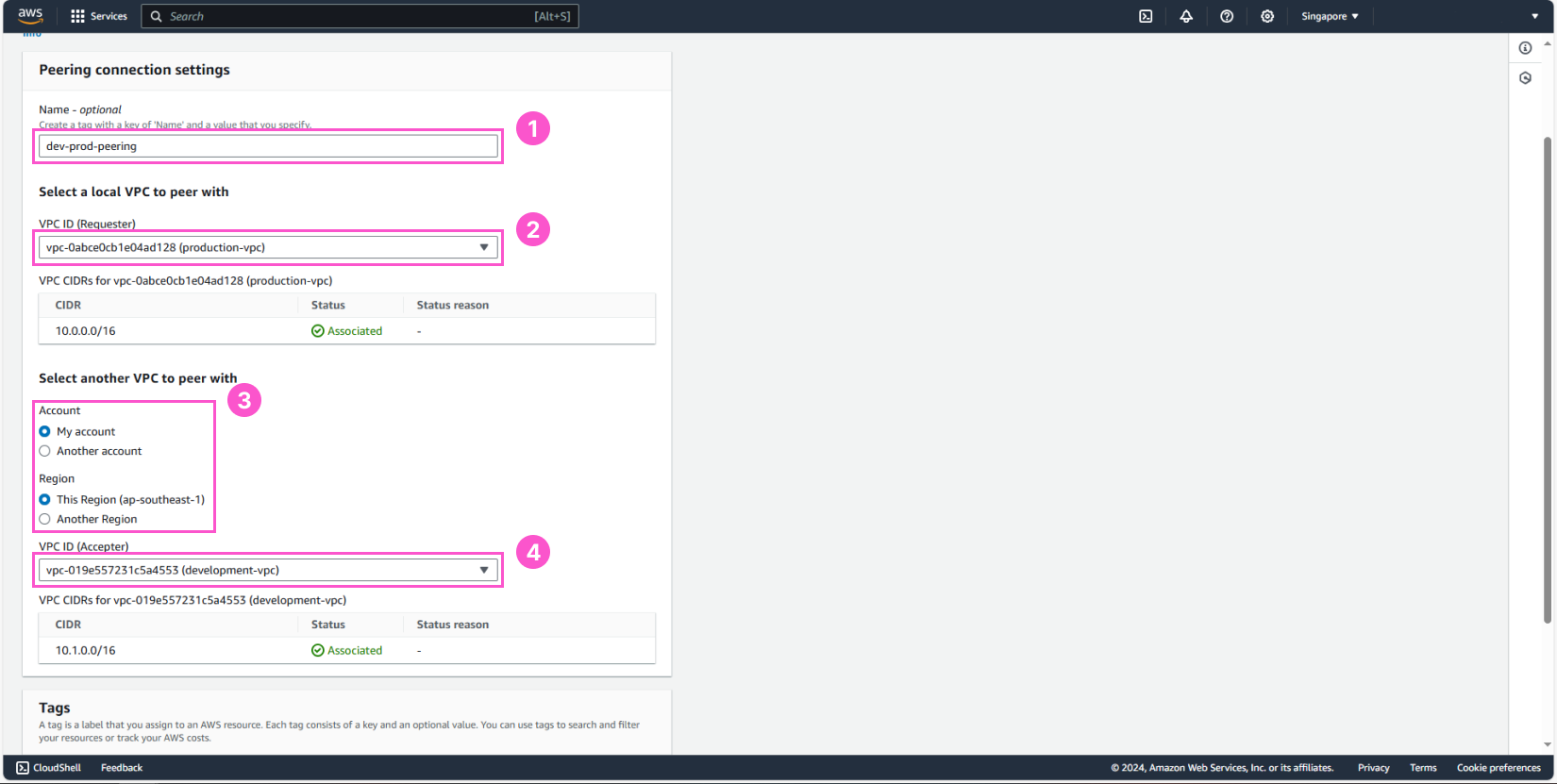
After creating it, we need to accept the newly established peering connection.
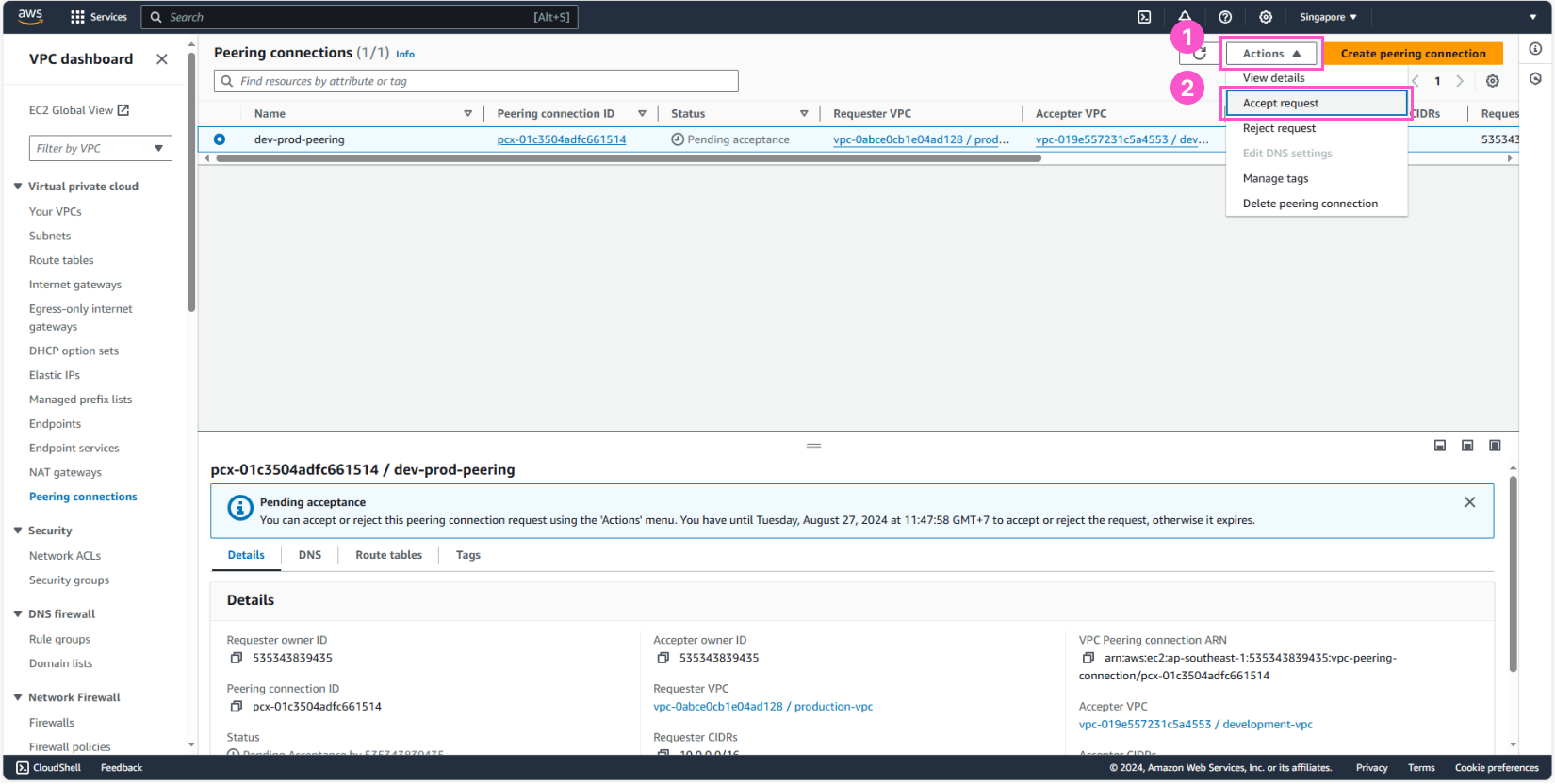
Configure route tables in both VPCs
At this point, the two VPCs have a “path” through the peering connection, but to allow the devices in both environments to truly communicate with each other, we need to configure the route tables that were created in previous steps.
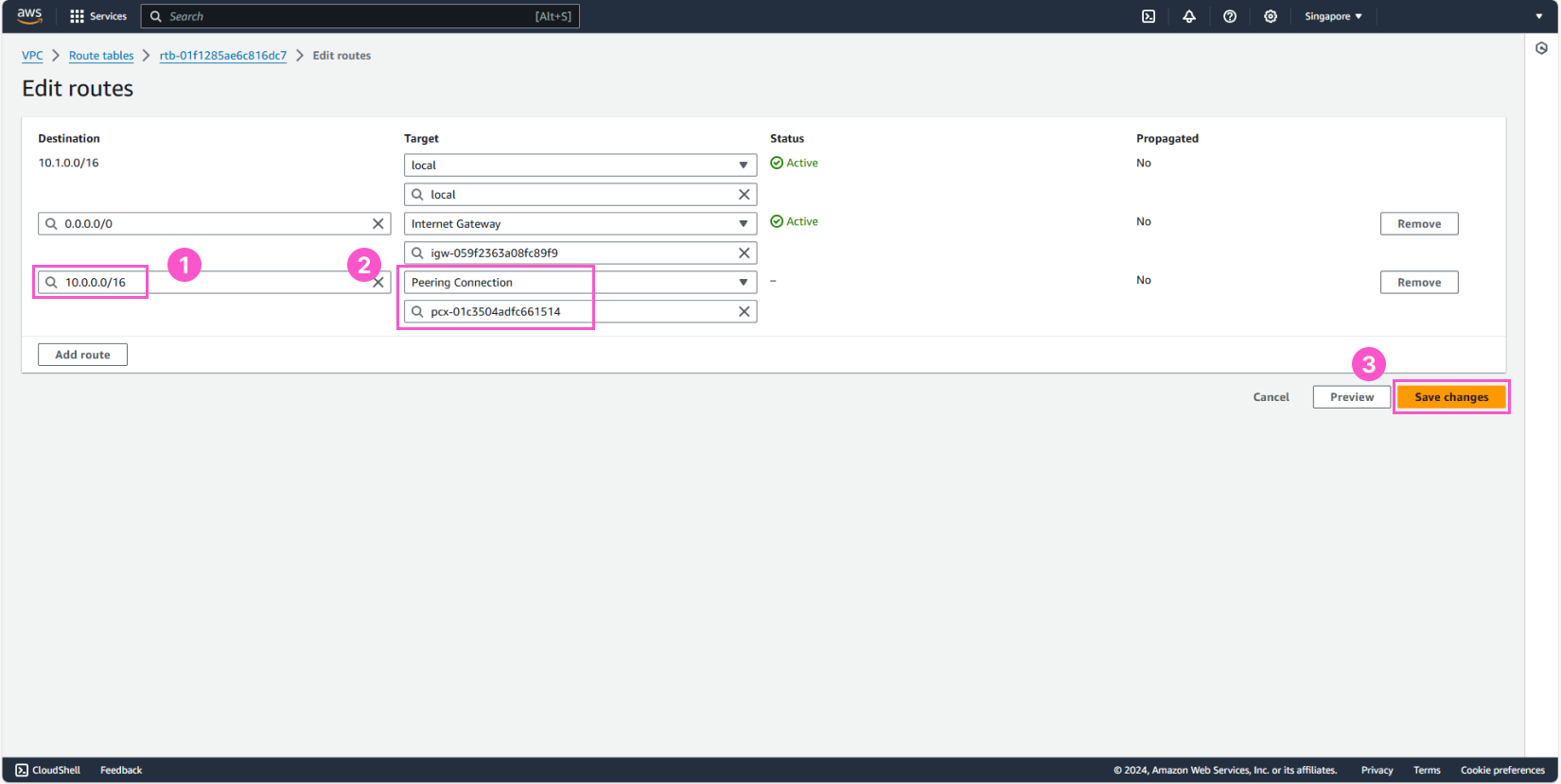
Now, go back to Route tables
- Select development-rtb-public
- In the bottom interface, choose the Routes tab
- Click Edit routes
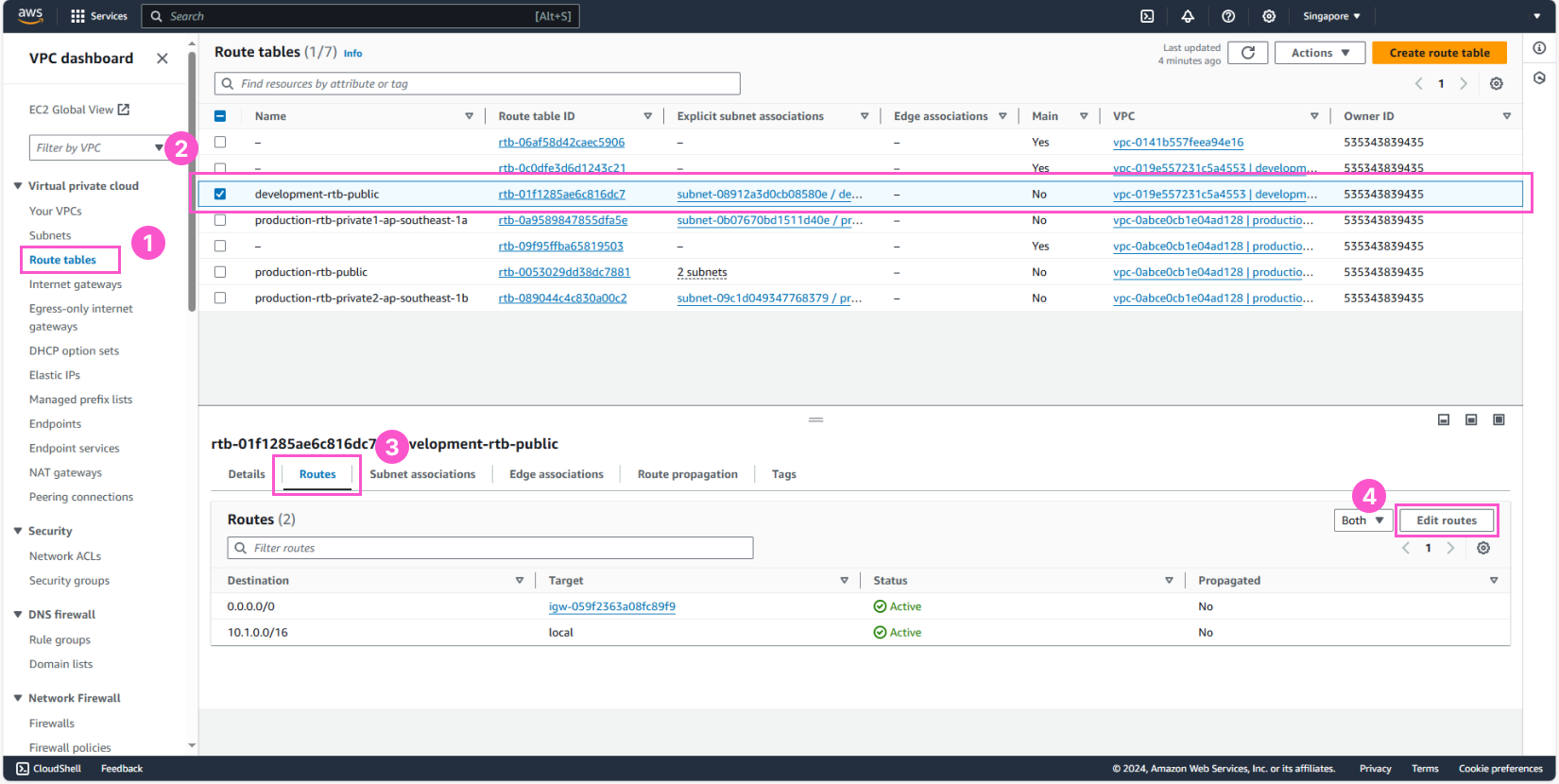
The IPv4 CIDR block for the development environment is 10.1.0.0/16, and for the production environment, it’s 10.0.0.0/16. To allow communication, we need to add the IPv4 CIDR block of the production environment, with the target being the Peering Connection that we just created.
Next:
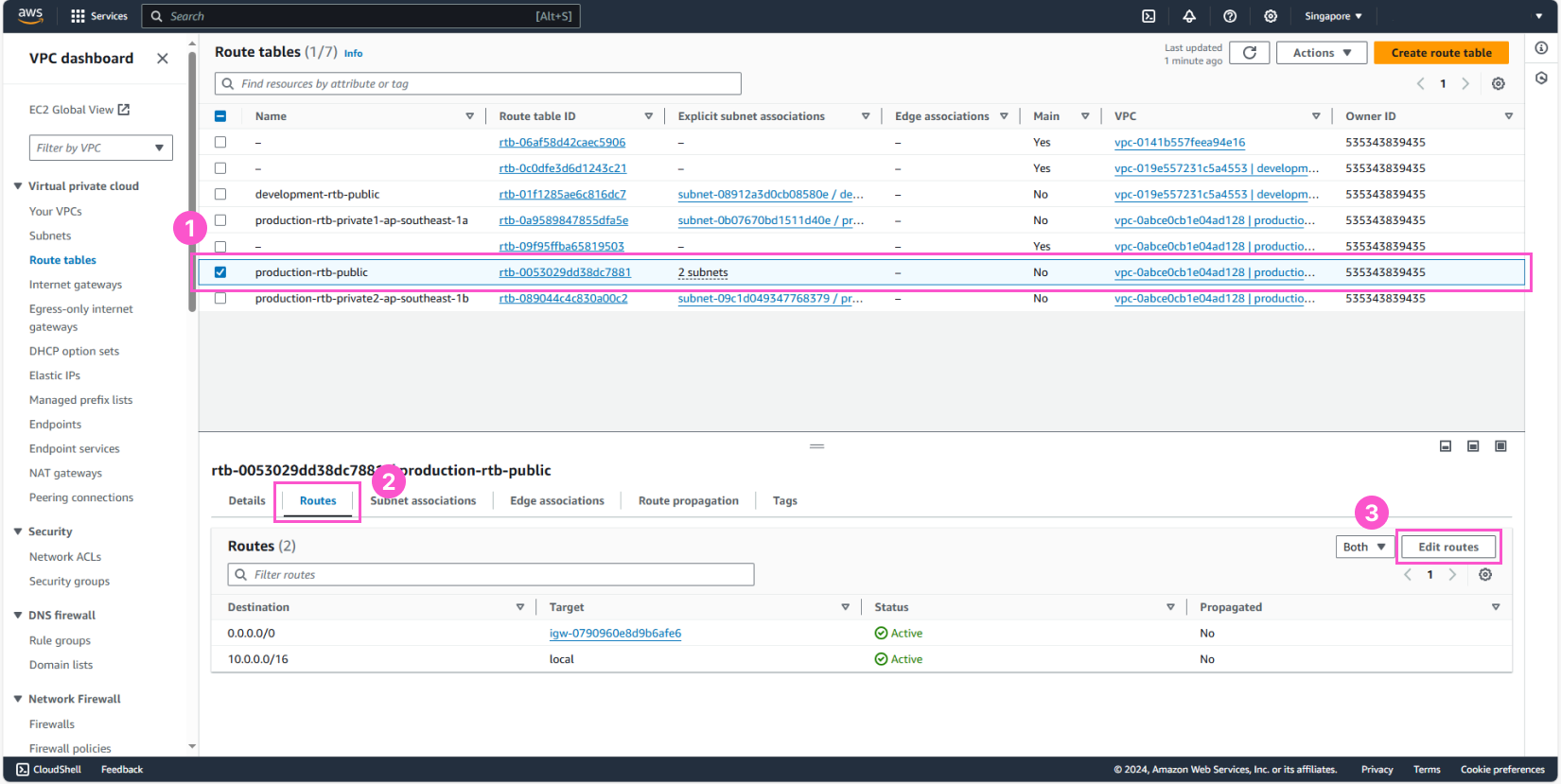
- Select production-rtb-public
- In the bottom interface, choose the Routes tab
- Click Edit routes
Here, similarly to the above, but we’ll do it in reverse.
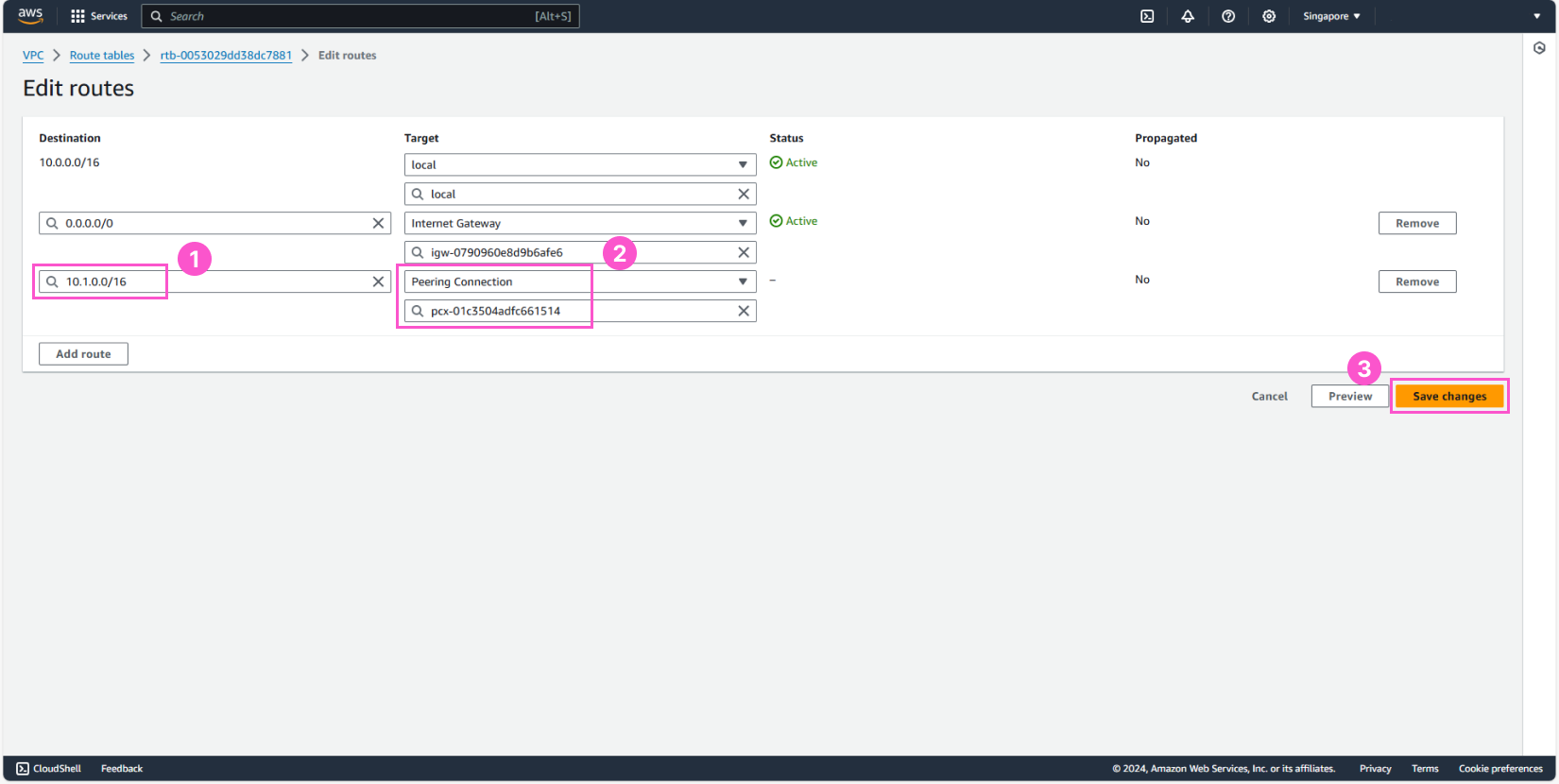
Once this setup is done, the EC2 instance in the public subnet of the development environment will be able to communicate with the EC2 instance in the private subnet of the production environment. However, the EC2 instance in the development environment cannot initiate communication with the EC2 instance in the production environment.