Create AWS Relational Database Service
AWS Relational Database Service
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) is a web service that makes it easier to set up, operate, and scale a relational database in the AWS Cloud.
Create a DB Instance on AWS
Note: The procedure below assumes that Standard create is enabled and Easy create is not. This procedure uses MySQL as an example.
Steps to create a DB Instance:
Log in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at RDS Console.
In the top-right corner of the Amazon RDS console, select the AWS region where you want to create the DB Instance.
In the navigation pane, select Databases.
Click Create database, then choose Standard create.
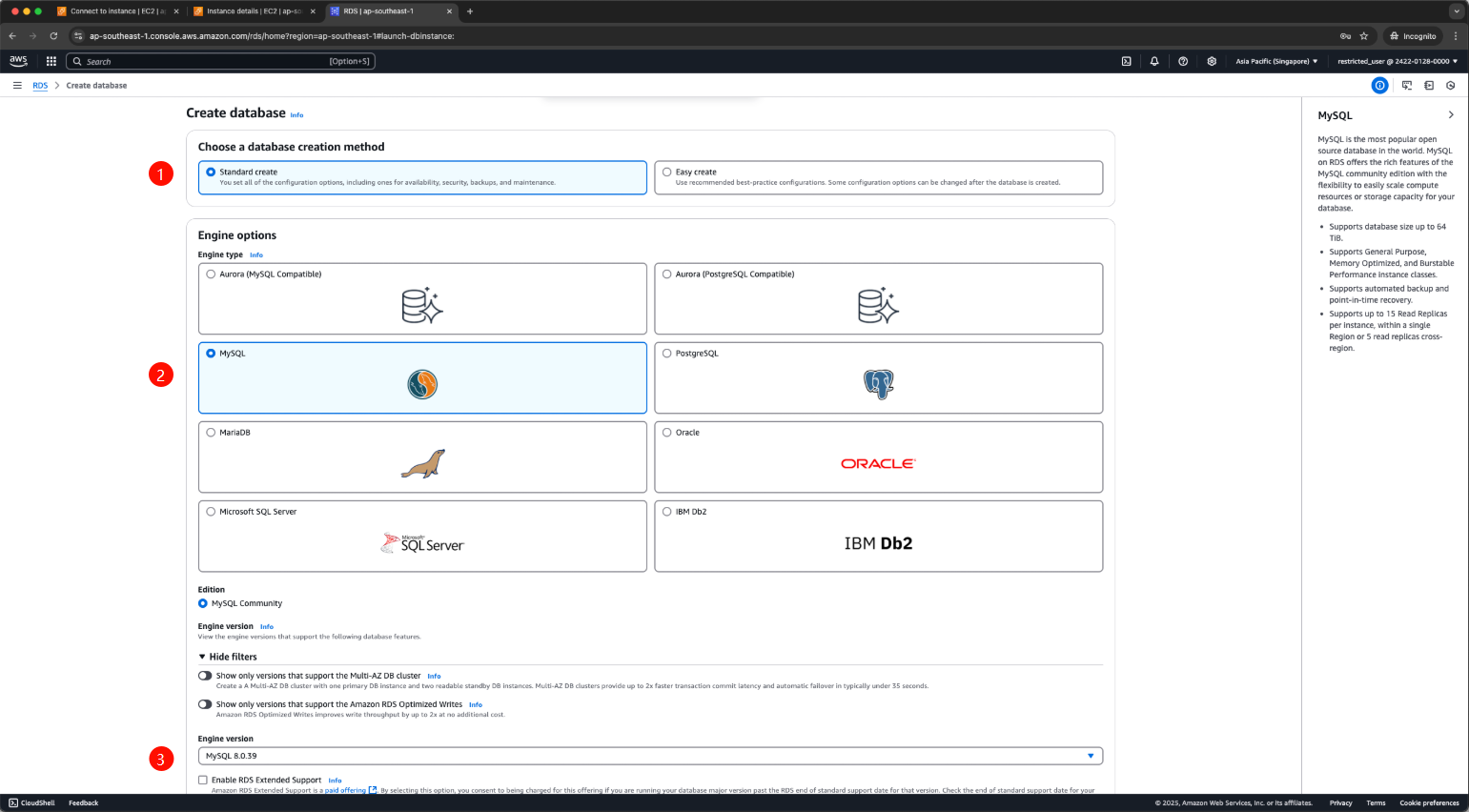
For Engine type, select MariaDB, Microsoft SQL Server, MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL. In this example, we use MySQL.
For Edition, select MySQL Community.
For Version, select the engine version (e.g., MySQL 8.0.39).
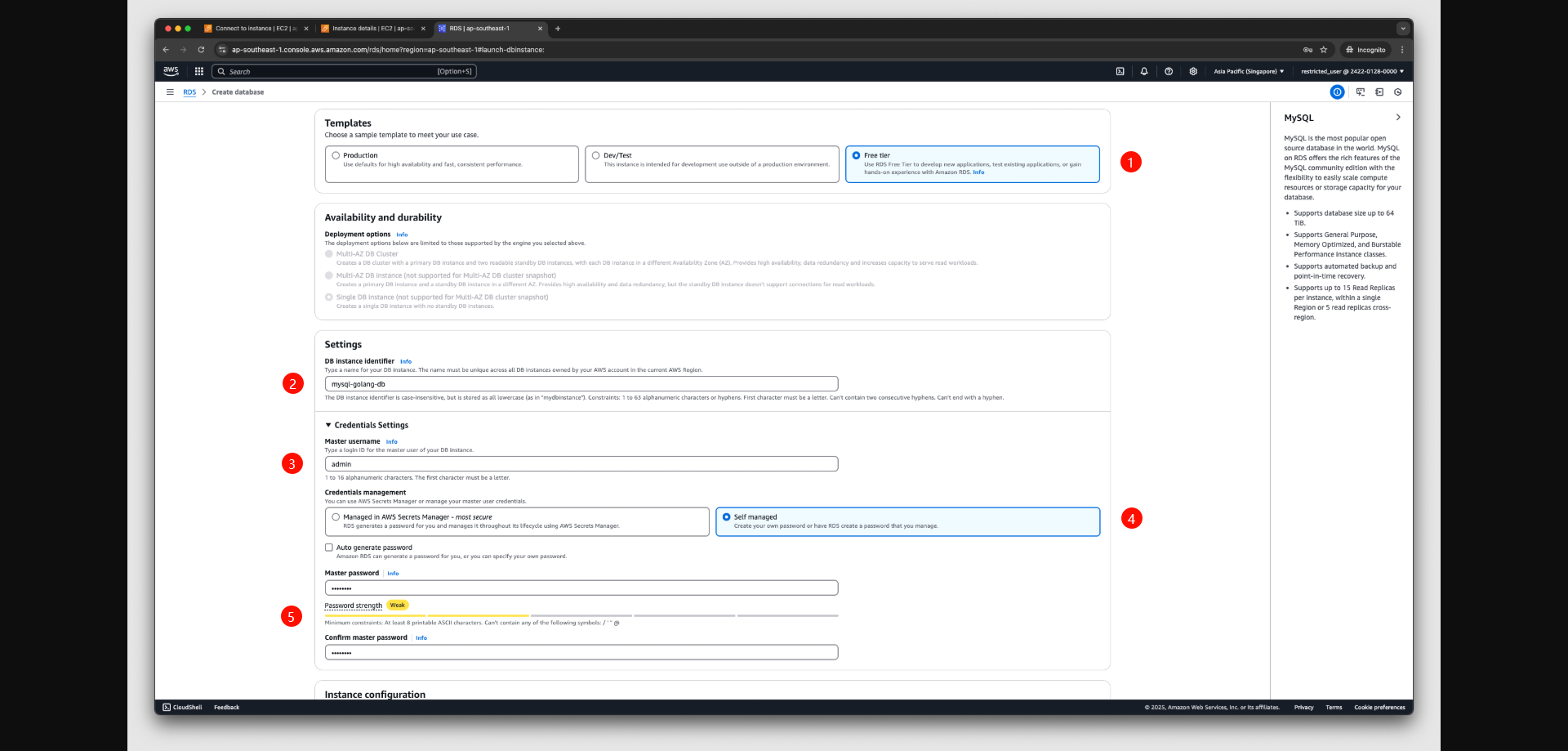
Under Templates, choose the Free tiers template.
To set the master password, follow these steps:
- In the Settings section, open Credential Settings.
- If Auto generate a password is checked, uncheck it if you want to specify a password.
- (Optional) Change the Master username value.
- Enter the same password in Master password and Confirm password.
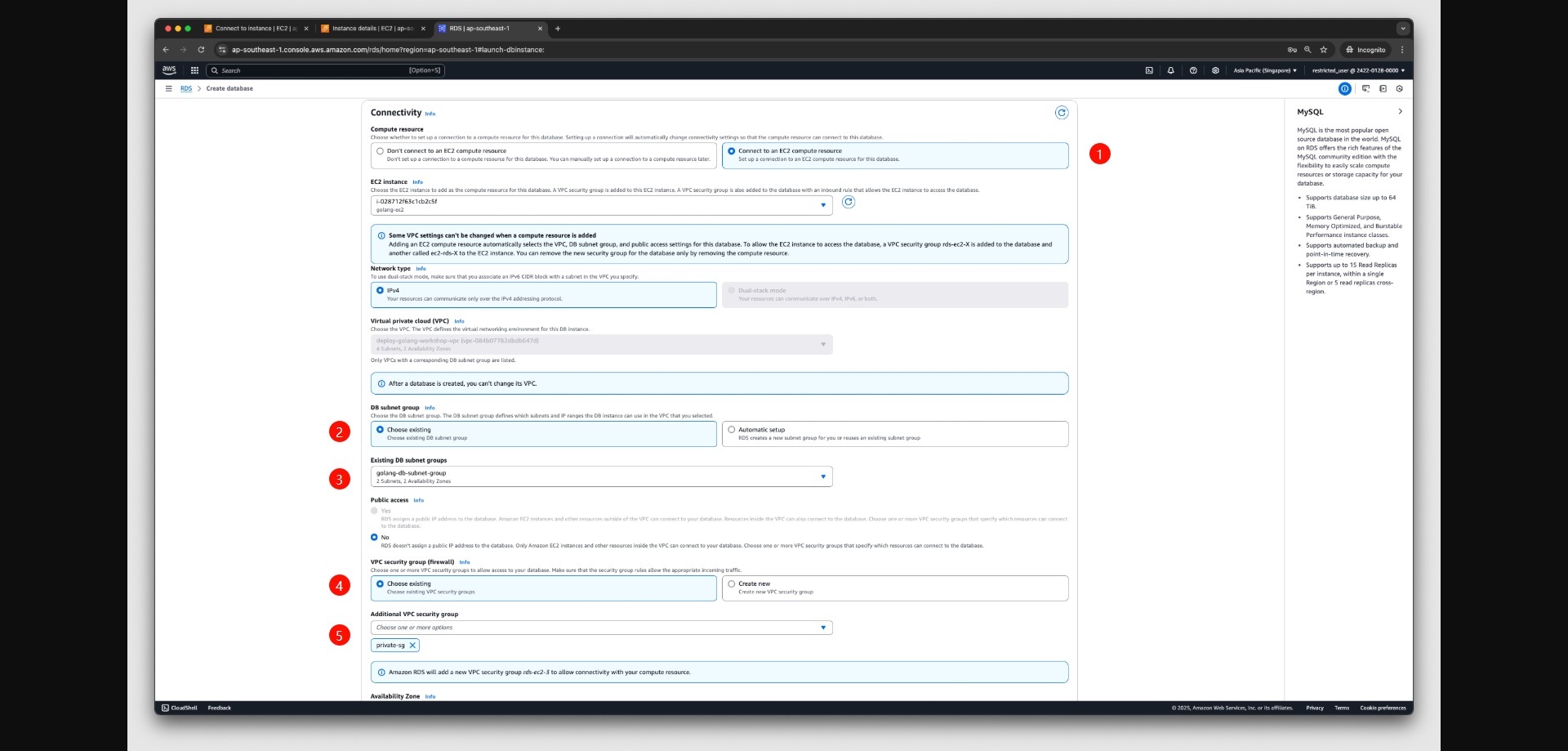
- (Optional) Set up connection with a compute resource for the DB Instance.
- You can configure the connection between an Amazon EC2 instance and the new DB Instance during the creation process.
- Under Connectivity, choose Connect to EC2 Compute Resource.
- Select the EC2 Instance you created earlier.
- Configure DB Subnet Group:
- In the DB Subnet Group section, choose Choose Existing and select golang-db-subnet-group.
- Configure VPC Security Group:
- Select Choose Existing, and from the dropdown, select private-sg, the security group you created earlier.
Click Create database.
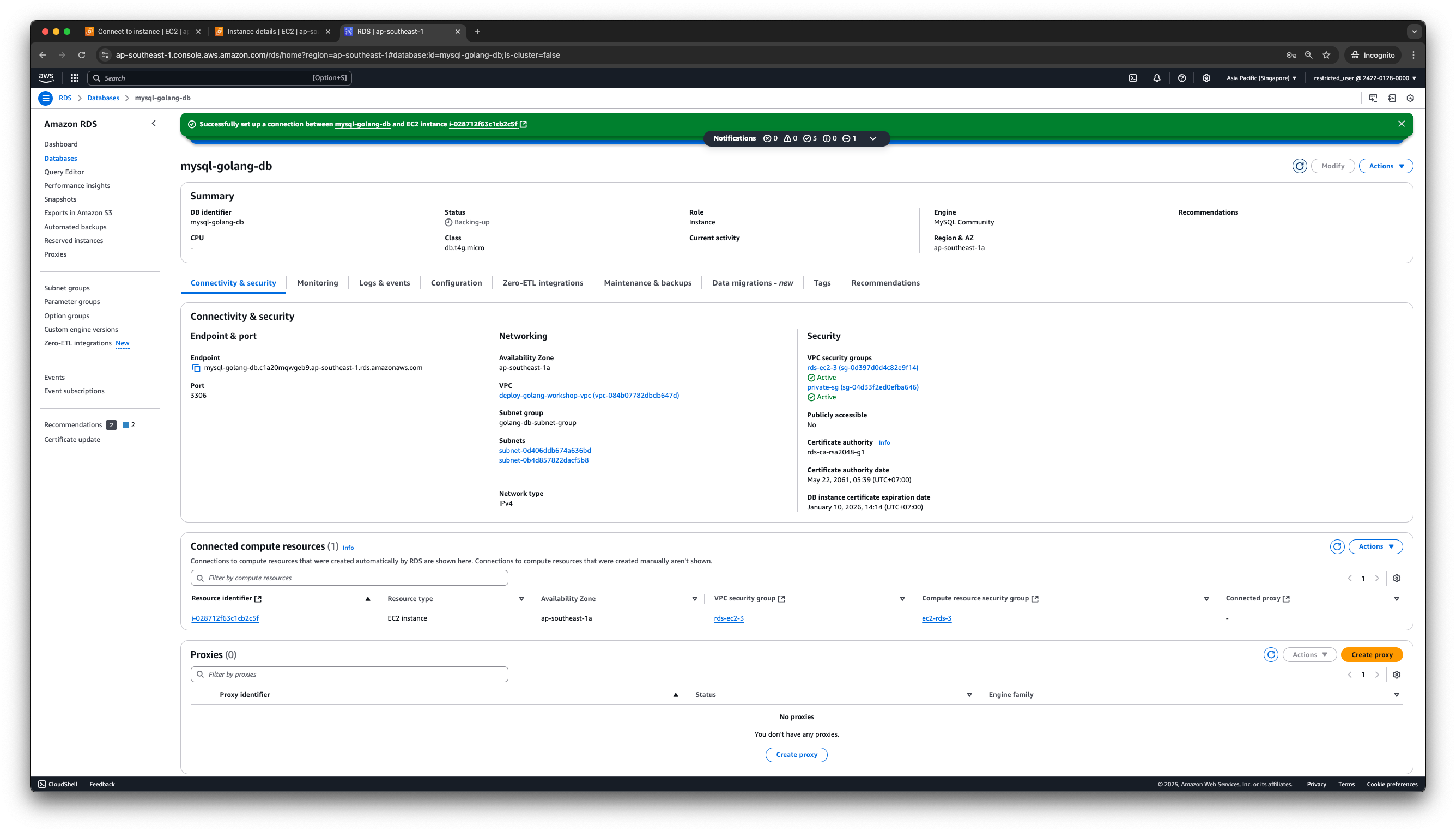
Verify the RDS Instance:
- In the RDS instance details page, you can find information like Endpoint, Port, and Username.
- The Endpoint is the URL or IP address you use to connect to the RDS database.
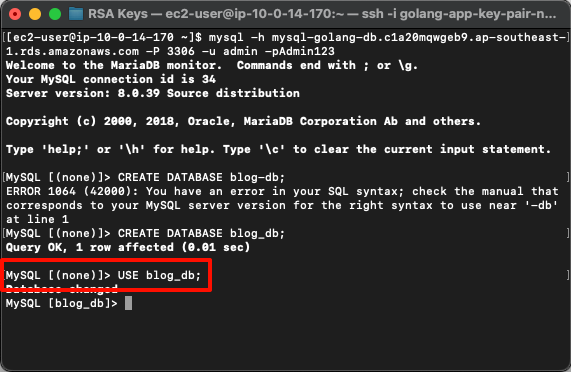
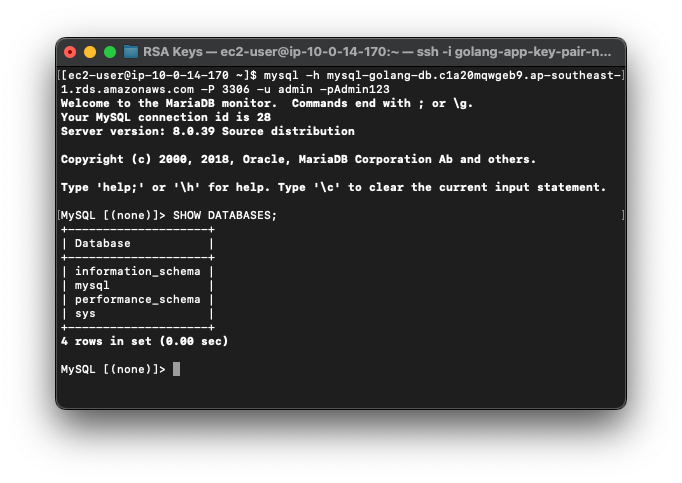
- Verify MySQL connection from EC2:
$ sudo yum install mysql
$ mysql -h <endpoint> -P 3306 -u admin -p <password>
# $ mysql -h mysql-golang-db.c1a20mqwgeb9.ap-southeast-1.rds.amazonaws.com -P 3306 -u admin -pAdmin123
- Create a Database:
The admin user cannot directly access the mysql database. It is recommended to create a new database for access. This issue is due to RDS privileges.
Since RDS is a managed service, to maintain system integrity and stability, superuser privileges are not granted to even the master user of the DB instance. Therefore, errors like this are expected, as the RDS MySQL master user by default does not have ADMIN, ROLE_ADMIN, or SUPER privileges.
CREATE DATABASE blog_db;
# Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
- Access the Database: