Create a VPC Instance
Introduction to VPC
In this workshop, Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is used to create a private network, enabling the organization and management of resources within a dedicated network space on AWS.
VPC allows you to have complete control over your network environment, including IP address configuration, route tables, internet gateways, and subnets.
Key Use Cases of VPC in the Workshop
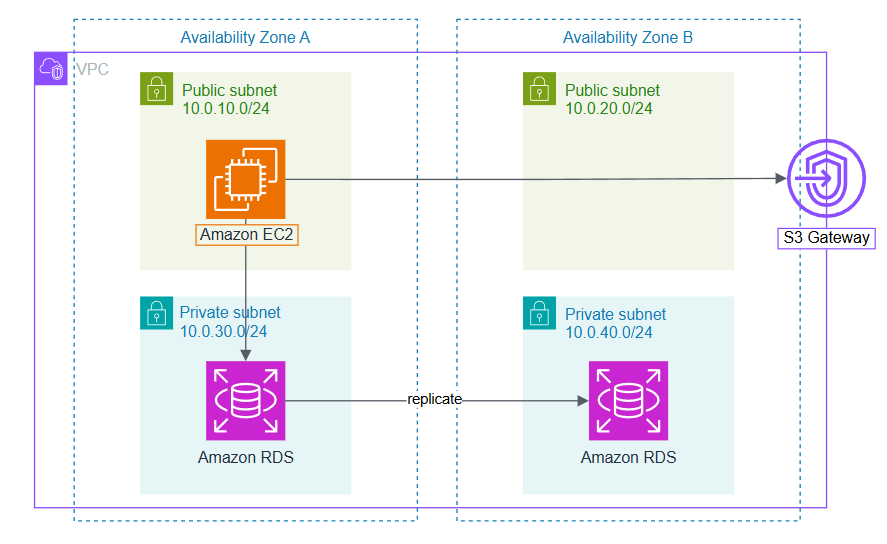
Hosting and running applications on EC2: Provides a secure environment for deploying virtual servers (instances).
Interacting with RDS databases: Creates a private subnet to protect the database from internet access, allowing connections only from services within the VPC.
Using S3 via Gateway: Ensures secure data transmission between S3 and services in the VPC through an S3 Gateway without exposing it to the public internet.
Pricing for VPC
There’s no additional charge for using a VPC. However, charges for some VPC components, such as NAT gateways, IP Address Manager, traffic mirroring, Reachability Analyzer, and Network Access Analyzer.
Create a VPC Instance
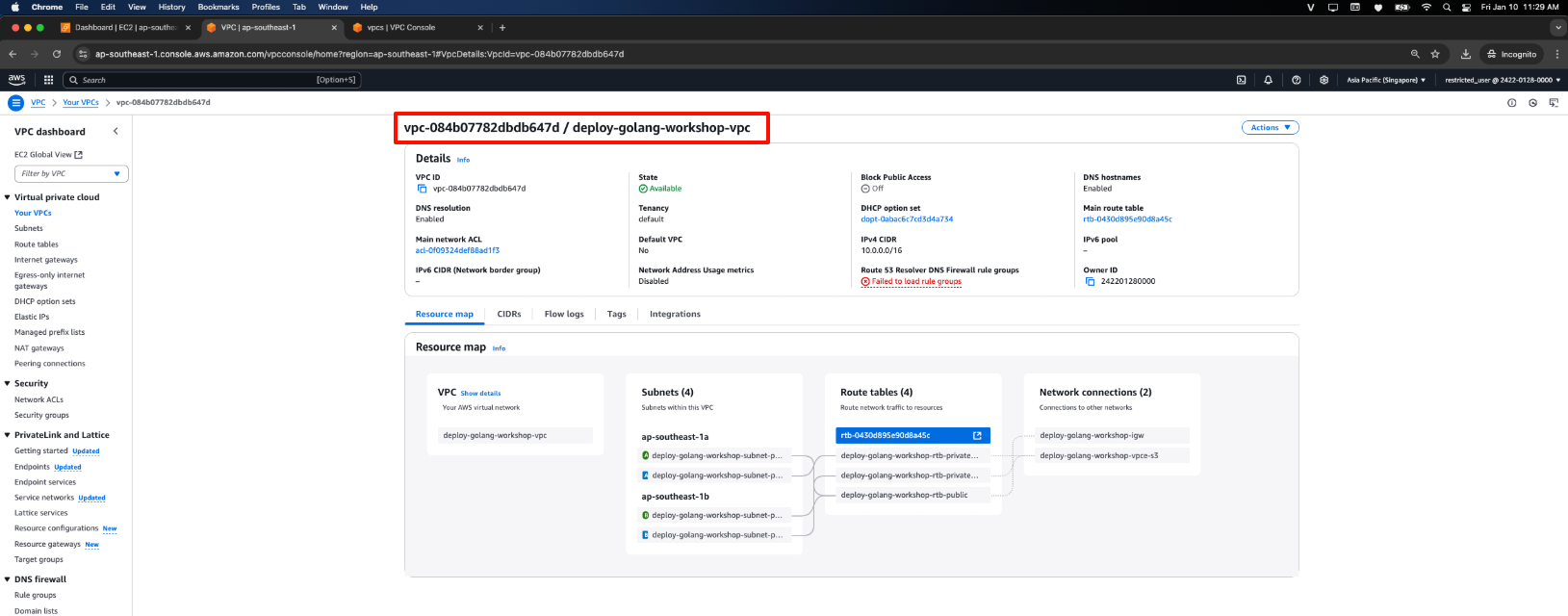
In this section, we will create a VPC Instance, which includes 2 Availability Zones (AZs), 2 Public Subnets and 2 Private Subnets.
1. Create the VPC Instance
- Go to Your VPCs, and select Create VPC.
- In the VPC Settings, choose the option VPC and more.
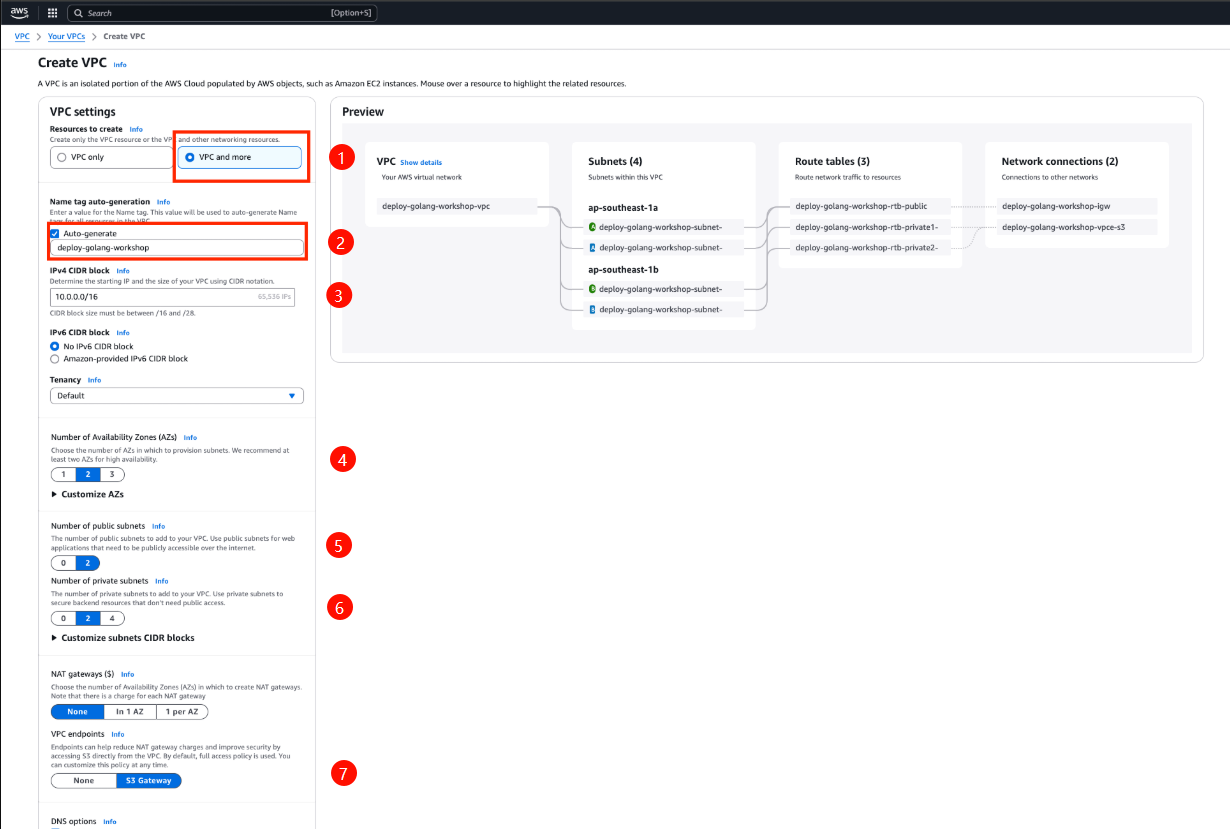
- Add a name tag and keep the default values for other fields, then click Create VPC.
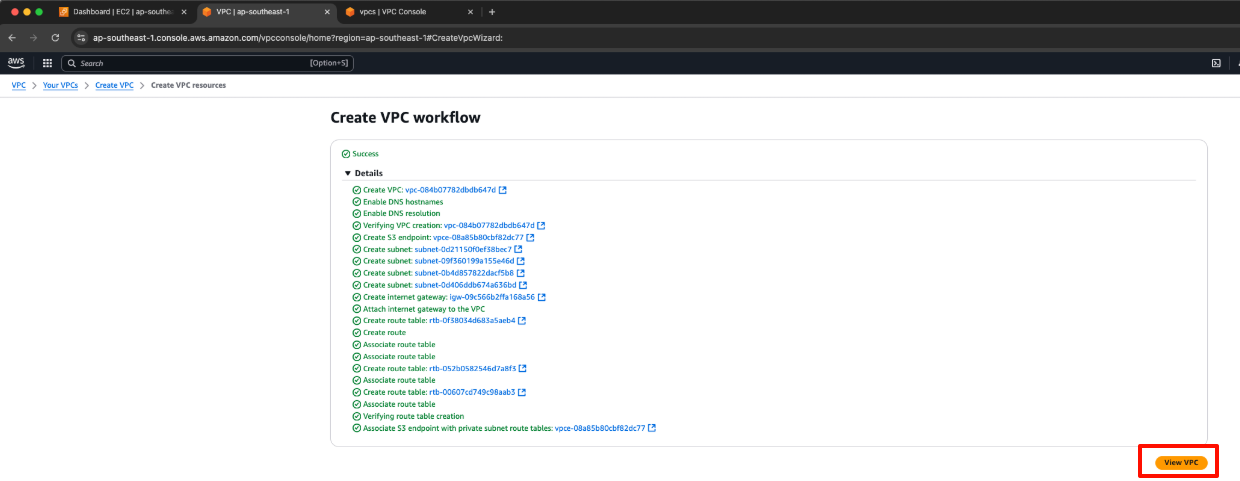
- The VPC Instance is successfully created.
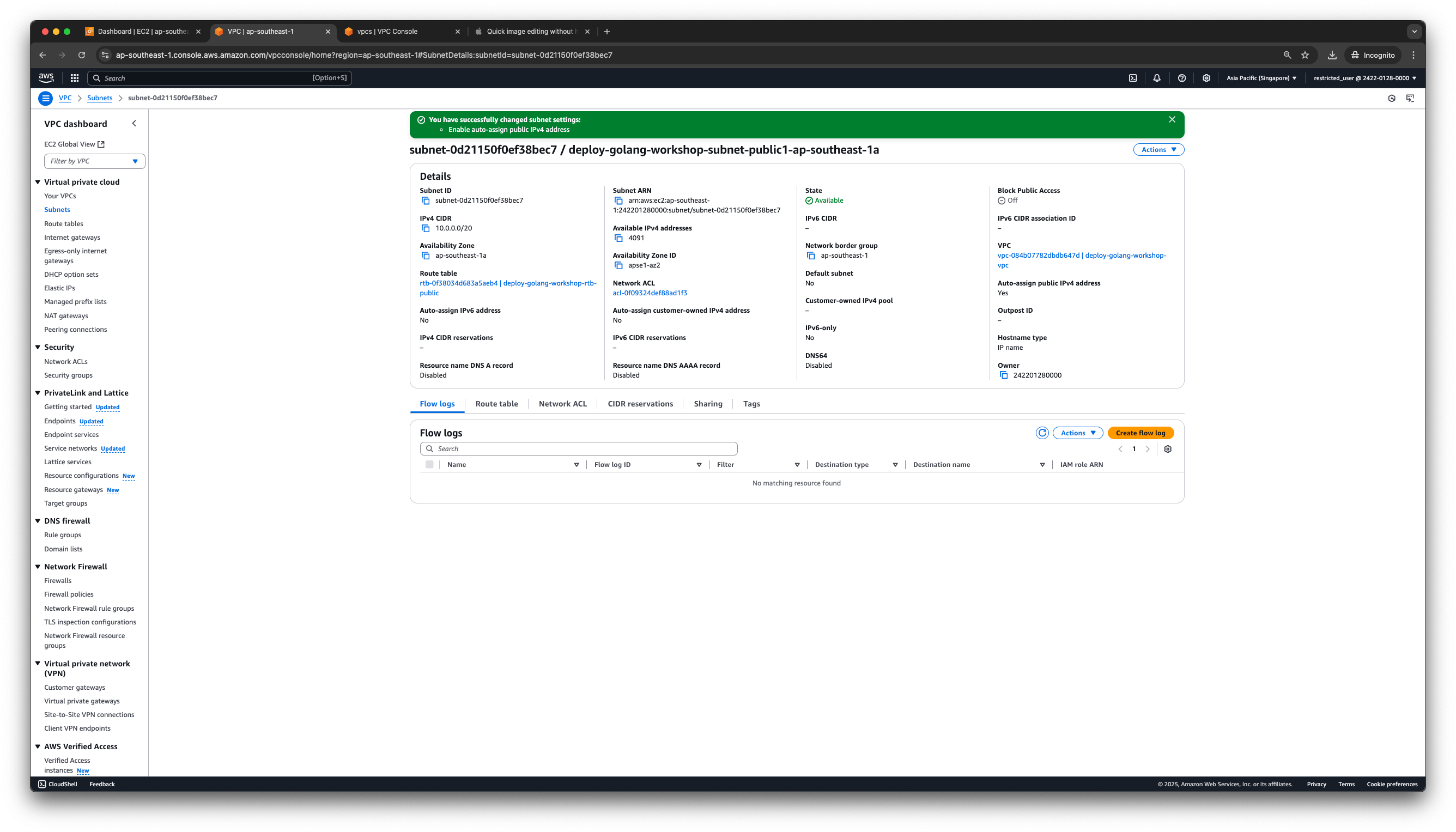
2. Assign Public IPv4 to Public Subnets
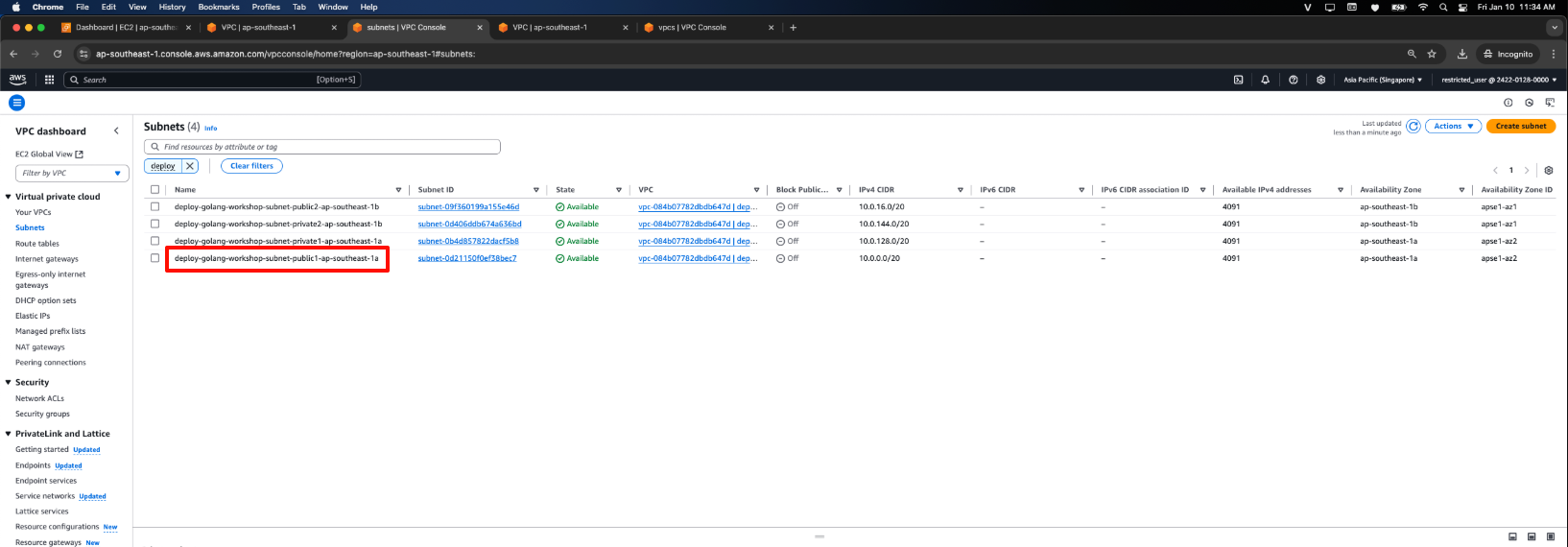
- Go to Subnets.
- Select the Subnet ID of the public subnet, e.g., deploy-golang-workshop-subnet-public1-ap-southeast-1a.
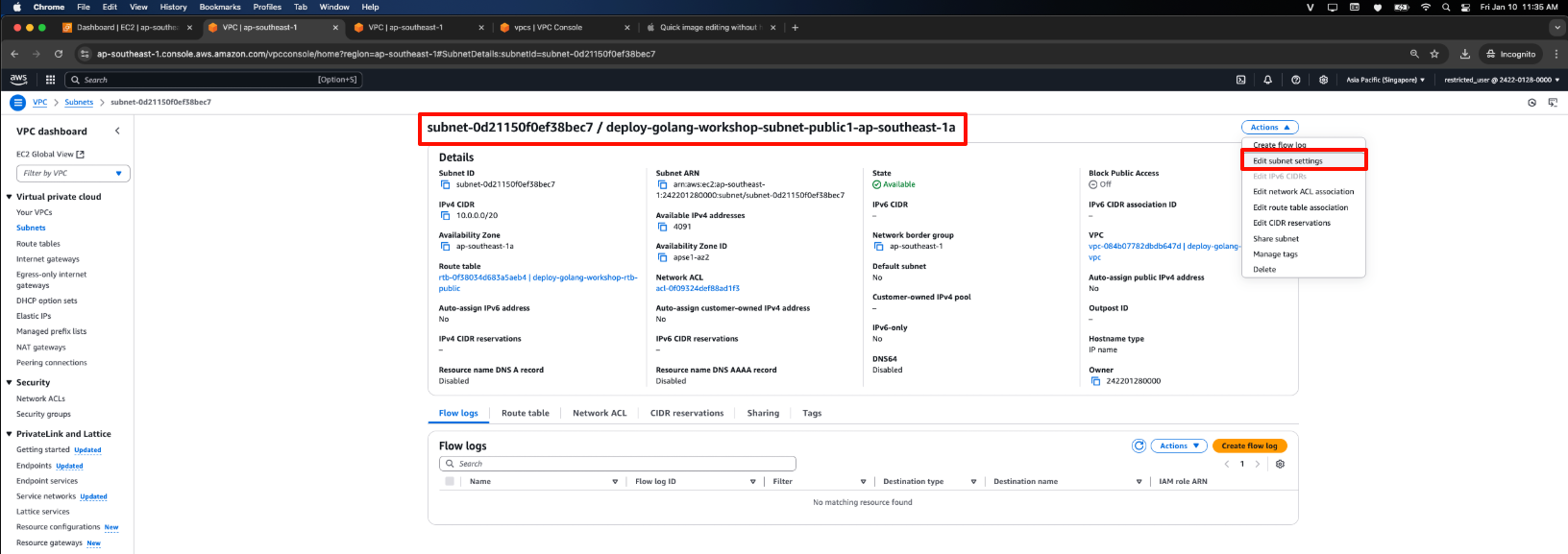
- From the dropdown Actions, choose Edit subnet settings.
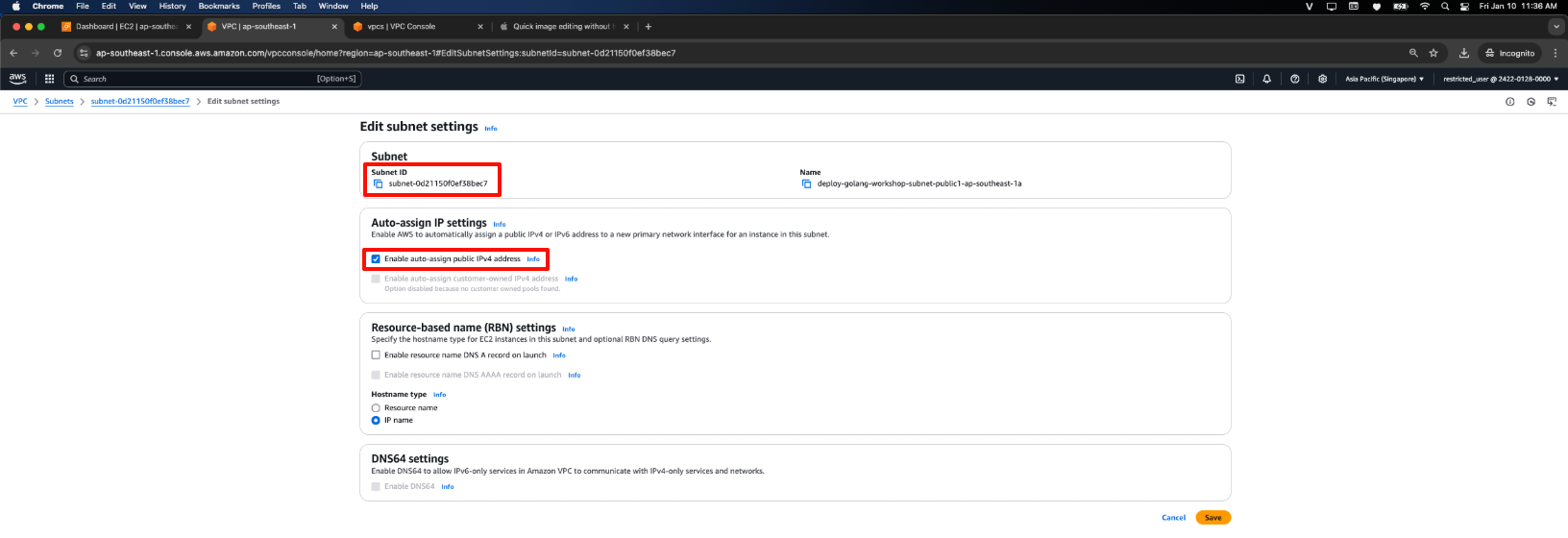
- Check the option Enable auto-assign public IPv4 address, and click Save.
- Successfully assigned a Public IPv4 address to the public subnet deploy-golang-workshop-subnet-public1-ap-southeast-1a.