Introduction
Canary Deployment is an application deployment strategy that helps minimize risk by rolling out a new version to a small subset of users before applying it to the entire system. With the growth of microservices and DevOps practices, Canary Deployment has become a popular and effective method for deploying applications safely and efficiently.
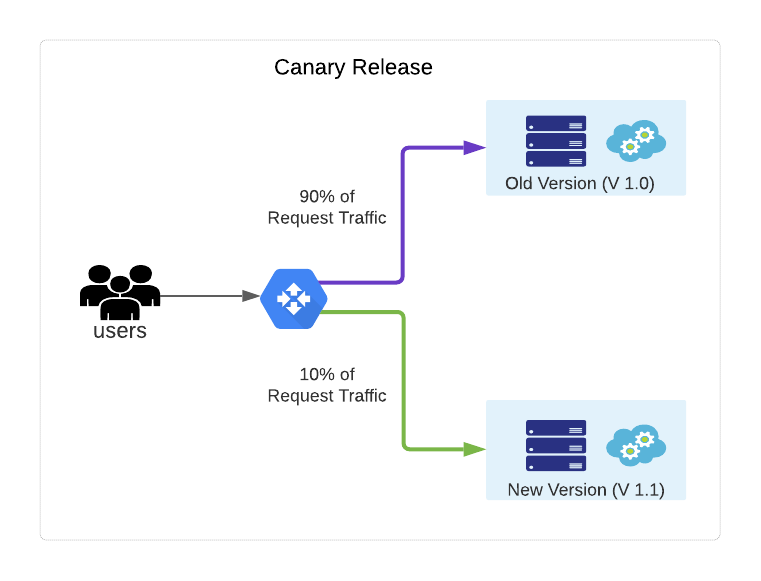
How Canary Deployment Works
Deploy the new version: Deploy the new version and run it in parallel with the old version.
Shift a small portion of traffic: Route a small percentage of incoming traffic (typically 1–5%) to the new version.
Test and monitor: Test and monitor the new version under real production conditions.
Shift all traffic: If the new version works as expected, gradually shift all traffic to the new version.
Canary Deployment can be implemented in two steps (two-step) or linearly (linear):
Two-step: Deploy the new version → expose it to a small user group → if it passes validation → roll it out to the entire environment.
Linear: Gradually increase the traffic to the new version in increments until all users are served by the new release.
Why Use It
Reduce downtime: Detect issues early with a small user group.
Automatic rollback: If errors occur, the system can automatically redirect traffic back to the stable version.
Flexible traffic management: Route traffic intelligently using an Application Load Balancer (ALB).
A/B Testing: Compare the performance of different versions in parallel.
Monitoring & Performance Analysis: Continuously collect metrics, monitor health, and make data-driven rollout decisions.